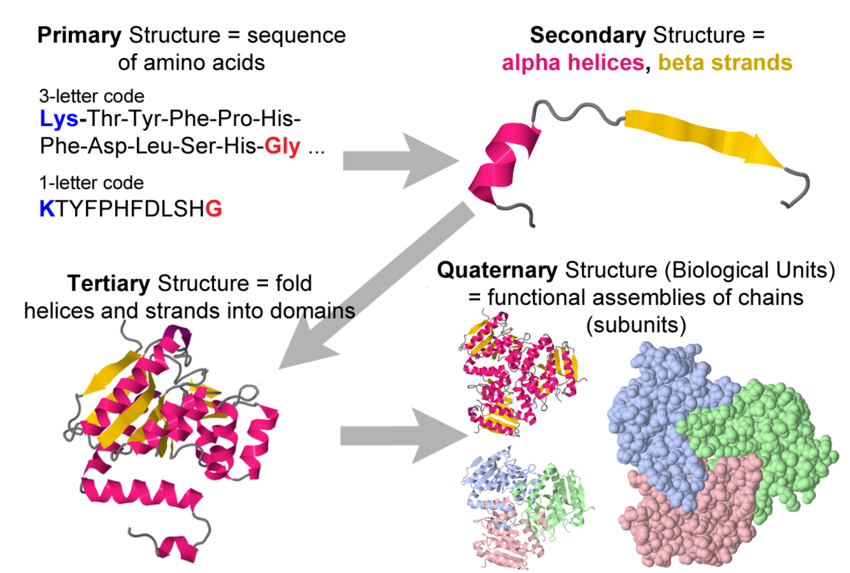
Protein Structure Tertiary . Web what is the tertiary structure of proteins? Web the tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. There are several ways this can happen. At this level, every protein has a. Web what holds a protein into its tertiary structure? Web the tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i.e., distinct compact folding.
from
Web what holds a protein into its tertiary structure? Web the tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i.e., distinct compact folding. Web the tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. At this level, every protein has a. There are several ways this can happen. Web what is the tertiary structure of proteins?
Protein Structure Tertiary At this level, every protein has a. Web what holds a protein into its tertiary structure? Web what is the tertiary structure of proteins? Web the tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i.e., distinct compact folding. There are several ways this can happen. At this level, every protein has a. Web the tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional.
From
Protein Structure Tertiary Web the tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i.e., distinct compact folding. Web what is the tertiary structure of proteins? There are several ways this can happen. At this level, every protein has a. Web the tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. Web what holds a protein into its tertiary structure? Protein Structure Tertiary.
From
Protein Structure Tertiary At this level, every protein has a. Web the tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i.e., distinct compact folding. Web what is the tertiary structure of proteins? Web what holds a protein into its tertiary structure? Web the tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. There are several ways this can happen. Protein Structure Tertiary.
From
Protein Structure Tertiary Web what is the tertiary structure of proteins? Web the tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i.e., distinct compact folding. Web the tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. At this level, every protein has a. There are several ways this can happen. Web what holds a protein into its tertiary structure? Protein Structure Tertiary.
From
Protein Structure Tertiary There are several ways this can happen. Web what holds a protein into its tertiary structure? Web the tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. At this level, every protein has a. Web what is the tertiary structure of proteins? Web the tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i.e., distinct compact folding. Protein Structure Tertiary.
From
Protein Structure Tertiary Web what holds a protein into its tertiary structure? Web what is the tertiary structure of proteins? At this level, every protein has a. Web the tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. There are several ways this can happen. Web the tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i.e., distinct compact folding. Protein Structure Tertiary.
From
Protein Structure Tertiary Web the tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. At this level, every protein has a. Web what holds a protein into its tertiary structure? There are several ways this can happen. Web the tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i.e., distinct compact folding. Web what is the tertiary structure of proteins? Protein Structure Tertiary.
From
Protein Structure Tertiary At this level, every protein has a. Web the tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. There are several ways this can happen. Web the tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i.e., distinct compact folding. Web what is the tertiary structure of proteins? Web what holds a protein into its tertiary structure? Protein Structure Tertiary.
From
Protein Structure Tertiary Web what is the tertiary structure of proteins? Web the tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i.e., distinct compact folding. Web what holds a protein into its tertiary structure? Web the tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. At this level, every protein has a. There are several ways this can happen. Protein Structure Tertiary.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Protein Tertiary Structure PowerPoint Presentation, free download Protein Structure Tertiary Web what is the tertiary structure of proteins? At this level, every protein has a. There are several ways this can happen. Web the tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. Web what holds a protein into its tertiary structure? Web the tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i.e., distinct compact folding. Protein Structure Tertiary.
From brunokruwwolf.blogspot.com
Which Best Describes the Tertiary Structure of a Protein BrunokruwWolf Protein Structure Tertiary Web the tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. At this level, every protein has a. There are several ways this can happen. Web the tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i.e., distinct compact folding. Web what holds a protein into its tertiary structure? Web what is the tertiary structure of proteins? Protein Structure Tertiary.
From
Protein Structure Tertiary Web what holds a protein into its tertiary structure? At this level, every protein has a. There are several ways this can happen. Web the tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. Web the tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i.e., distinct compact folding. Web what is the tertiary structure of proteins? Protein Structure Tertiary.
From
Protein Structure Tertiary At this level, every protein has a. Web what holds a protein into its tertiary structure? Web the tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i.e., distinct compact folding. Web what is the tertiary structure of proteins? There are several ways this can happen. Web the tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. Protein Structure Tertiary.
From
Protein Structure Tertiary There are several ways this can happen. At this level, every protein has a. Web the tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. Web the tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i.e., distinct compact folding. Web what is the tertiary structure of proteins? Web what holds a protein into its tertiary structure? Protein Structure Tertiary.
From www.researchgate.net
The tertiary structure of the T391A protein. A, a ribbon drawing of the Protein Structure Tertiary Web the tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i.e., distinct compact folding. At this level, every protein has a. Web the tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. There are several ways this can happen. Web what holds a protein into its tertiary structure? Web what is the tertiary structure of proteins? Protein Structure Tertiary.
From
Protein Structure Tertiary Web what is the tertiary structure of proteins? At this level, every protein has a. There are several ways this can happen. Web the tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. Web the tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i.e., distinct compact folding. Web what holds a protein into its tertiary structure? Protein Structure Tertiary.
From
Protein Structure Tertiary Web the tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. Web what is the tertiary structure of proteins? Web the tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i.e., distinct compact folding. At this level, every protein has a. Web what holds a protein into its tertiary structure? There are several ways this can happen. Protein Structure Tertiary.
From
Protein Structure Tertiary There are several ways this can happen. Web the tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. Web what holds a protein into its tertiary structure? At this level, every protein has a. Web the tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i.e., distinct compact folding. Web what is the tertiary structure of proteins? Protein Structure Tertiary.
From
Protein Structure Tertiary Web the tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i.e., distinct compact folding. Web the tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. Web what is the tertiary structure of proteins? There are several ways this can happen. At this level, every protein has a. Web what holds a protein into its tertiary structure? Protein Structure Tertiary.